Hybrid vs. Electric Vehicles: Which Is Right for You?
Amidst climate change and rising fuel costs, choosing an eco-friendly vehicle has never been more important. Hybrid, plug-in hybrid, and electric vehicles have emerged as leading contenders, poised to reshape the automotive industry. However, deciding which type of vehicle is right for you depends on various personal factors and driving habits. Let's explore and compare these three types of vehicles in detail to help you find the perfect match.
Category: Automotive
A Detailed Comparison: Hybrid vs. Plug-in Hybrid vs. Electric Vehicles
| Feature | Hybrid (HEV) | Plug-in Hybrid (PHEV) | Electric (EV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Operating Principle | Combines a gasoline engine with an electric motor; cannot be plugged in | Combines a gasoline engine with a larger electric motor and battery; can be plugged in to recharge | Runs entirely on electricity; must be plugged in to recharge |
| Fuel Efficiency | More fuel-efficient than traditional gasoline cars | Highly fuel-efficient, especially for shorter trips that can be done on electricity alone | No fuel consumption, low running costs |
| Range | Long, similar to traditional gasoline cars | Moderate electric-only range (20-50 miles), then functions as a hybrid | Dependent on battery capacity (typically 150-300+ miles) |
| Refueling/Recharging Time | No charging is required, refuels like a gasoline car | Several hours on a standard outlet, faster with a dedicated charger | Varies greatly depending on the charger type and battery capacity (30 minutes to several hours) |
| Price | Generally lower than PHEVs and EVs | Typically priced between HEVs and EVs | Higher upfront cost compared to HEVs and PHEVs |
| Environmental Impact | Lower emissions compared to gasoline cars | Lower emissions than HEVs, potentially zero emissions for short trips | Zero tailpipe emissions |
| Infrastructure | Widespread gas stations available | Benefits from both gas stations and charging stations, but charging infrastructure is still developing | Reliant on charging stations, which are becoming increasingly common but still require planning for longer trips |
Hybrid Vehicles (HEVs): A Blend of Traditional and Modern
Hybrid cars, like the popular Toyota Prius and Honda Insight, utilize both a gasoline engine and an electric motor, offering benefits like improved fuel efficiency and extended range without needing to be plugged in. However, HEVs still produce some emissions and their engine efficiency might not be as high as plug-in hybrids or electric vehicles.
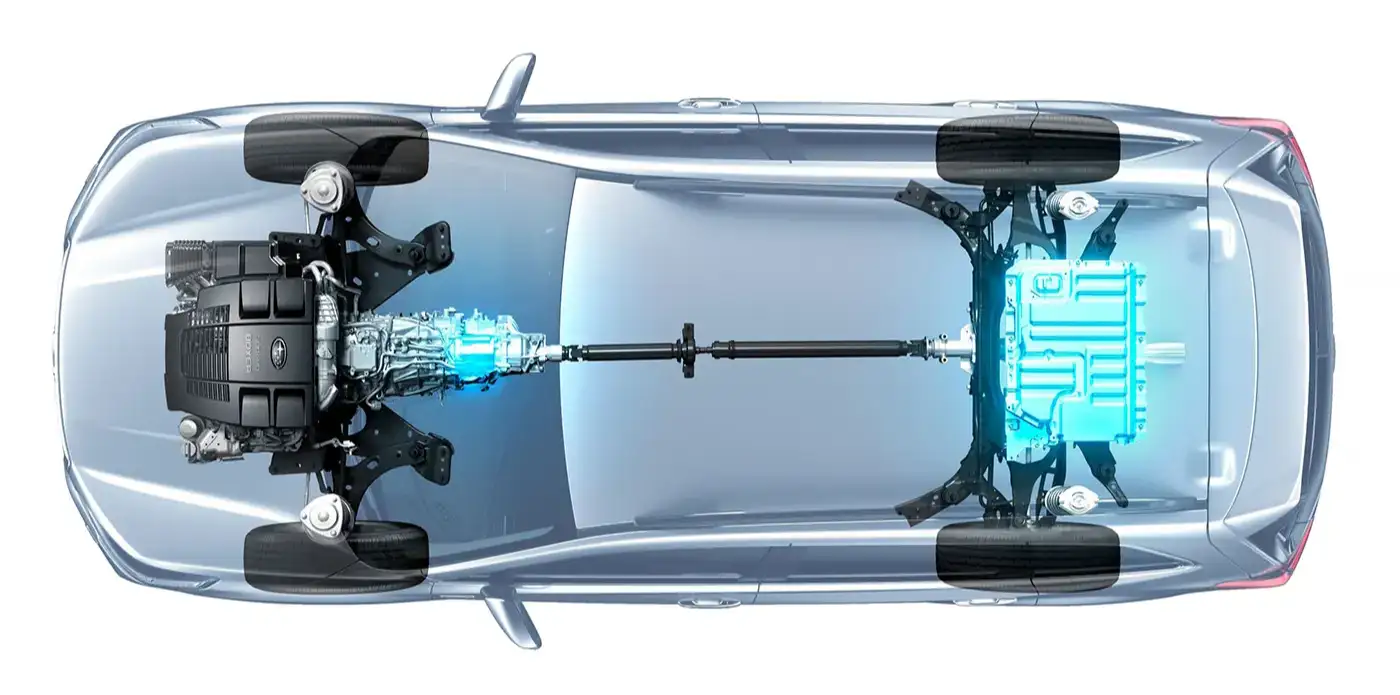
Pros:
- Significantly better fuel economy, reducing running costs.
- Extended range, eliminating range anxiety.
- Easy access to gas stations, no charging infrastructure concerns.
Cons:
- Still produce emissions, although less than gasoline cars.
- Engine efficiency may not be as high as PHEVs or EVs.
Plug-in Hybrids (PHEVs): Bridging the Gap
PHEVs, such as the Ford Escape PHEV and the Mitsubishi Outlander PHEV, offer the best of both worlds by combining a gasoline engine with a larger battery pack that can be charged externally. This allows for longer electric-only ranges, often sufficient for daily commutes, while still offering the flexibility of a gasoline engine for longer trips.
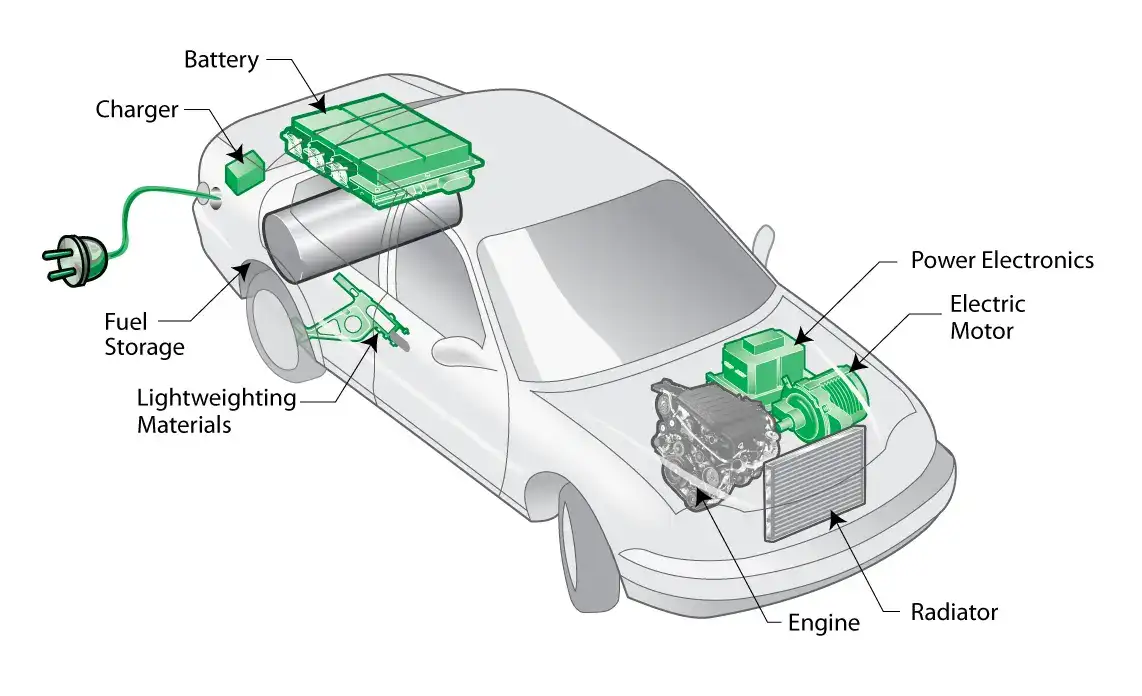
Electric Vehicles (EVs): The Future of Green Transportation
Electric vehicles, with frontrunners like the Tesla Model 3 and the Chevrolet Bolt, are the perfect choice for environmentally conscious individuals. With quiet operation, low running costs, and zero tailpipe emissions, EVs are gaining popularity. However, their range is often limited by battery capacity and charging times can be lengthy, making access to charging infrastructure crucial.
Pros:
- Environmentally friendly, with zero tailpipe emissions.
- High performance, with quick acceleration and smooth operation.
- Low running costs, requiring minimal maintenance.
Cons:
- Limited range compared to HEVs and gasoline cars, although improving.
- Long charging times require planning and patience.
- Charging infrastructure is still developing in many areas.
Battery Technology: Shaping the Future of EVs
Advancements in battery technology, particularly the development of solid-state batteries, hold immense potential for improving EV range and charging times. Solid-state batteries offer higher energy density, faster charging capabilities, and improved safety compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries, potentially revolutionizing the EV market shortly.
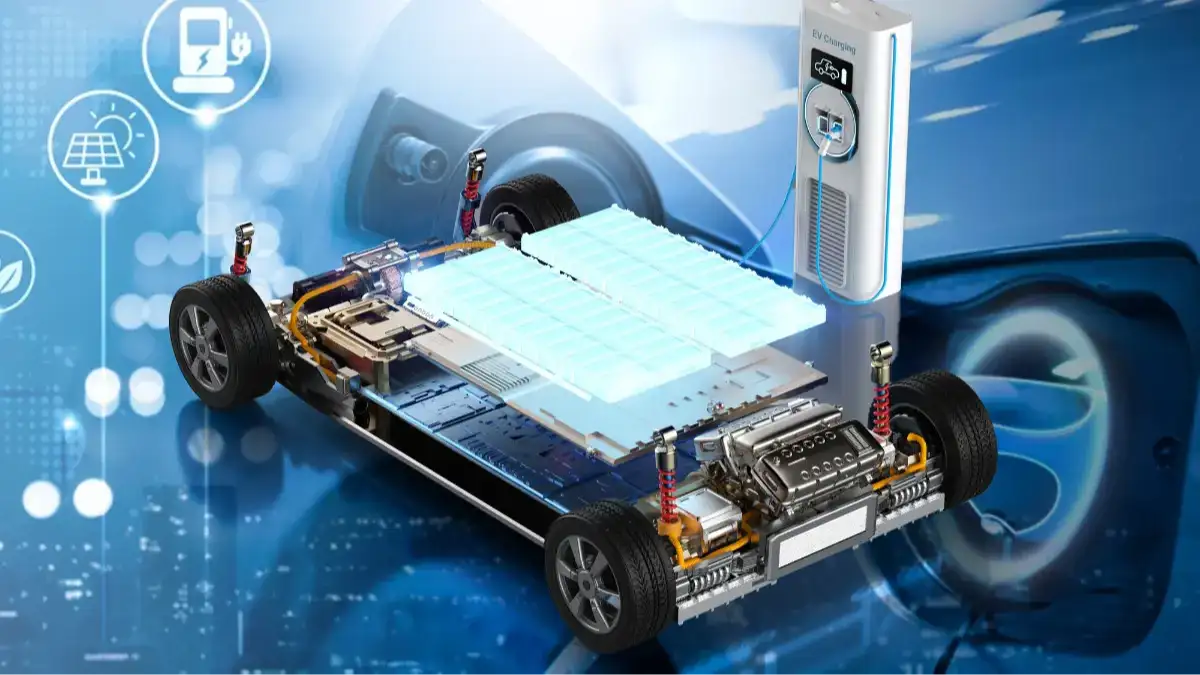

Charging Infrastructure: Challenges and Solutions
The widespread adoption of EVs is heavily reliant on a robust charging infrastructure. While public charging stations are becoming increasingly common, challenges remain in terms of availability, charging speeds, and grid capacity. Home charging offers convenience, but requires access to dedicated parking and appropriate electrical installations. Investing in faster charging technologies and expanding charging networks are crucial for accelerating EV adoption.
Government Incentives and Policies: Driving the Transition
Government policies and incentives play a pivotal role in promoting the adoption of hybrid, plug-in hybrid, and electric vehicles. Tax credits, rebates, and subsidies can make these vehicles more financially appealing to consumers. Additionally, policies such as emissions standards and zero-emission vehicle mandates encourage manufacturers to invest in and produce more eco-friendly vehicles. As governments around the world recognize the urgency of combating climate change, we can expect to see continued support and initiatives aimed at accelerating the transition to a more sustainable transportation future.
Choosing the Right Vehicle for You
The decision between a hybrid, plug-in hybrid, or an electric vehicle ultimately depends on your individual needs and circumstances. Consider your typical driving distances, access to charging infrastructure, budget, and environmental priorities.
Factors to Consider:
- Driving Needs: City driving or long journeys?
- Budget: How much are you willing to spend on a car?
- Incentives: Are there any government incentives for buying an EV or PHEV?
- Infrastructure: Is there convenient access to charging stations? Do you have home charging capabilities?
Conclusion
Hybrid, plug-in hybrid, and electric vehicles all offer unique advantages in terms of environmental protection and fuel efficiency. Choosing between them depends on your individual needs, financial situation, and the available infrastructure. Carefully consider these factors and choose the vehicle that best suits your lifestyle. After all, the perfect car is the one that best meets your needs!
